When it comes to automotive performance, the wheels of a vehicle play a crucial role in handling, speed, and safety. Different materials are used in the construction of wheels, each offering unique properties that can affect the vehicle’s performance. This comprehensive guide aims to clarify the terminology related to wheel construction materials, making it an essential resource for anyone interested in automotive mechanics, enthusiast modifications, or simply better understanding the components of a car.
The Importance of Wheel Materials
Wheels do not merely serve as the foundation on which a vehicle moves; their materials directly impact various performance aspects. This section discusses why wheel materials matter:
- Weight: The weight of the wheel affects acceleration and braking. Lighter wheels can enhance vehicle responsiveness and fuel efficiency.
- Strength: A wheel must withstand various stresses, from everyday driving to high-performance conditions. The material dictates the wheel’s durability and ability to handle forces.
- Heat Dissipation: Braking generates heat, and certain materials are better at dissipating this heat, which can help reduce brake fade.
- Aesthetic Appeal: The materials used can also influence the wheel’s appearance, contributing to the overall style of the vehicle.
Types of Wheel Construction Materials
Understanding the different materials used in wheel construction is pivotal for choosing the right wheels for a vehicle. Here are the most common types:
1. Steel Wheels
Steel wheels are often regarded as the workhorses of the automotive world. They are made from a solid sheet of steel and are known for their durability and affordability.
- Advantages:
- Cost-effective
- Highly durable
- Good for winter tires
- Disadvantages:
- Heavier than other materials
- Less aesthetically pleasing
- Prone to rust without proper coating
2. Aluminum Alloy Wheels
Aluminum alloy wheels are a popular choice among performance enthusiasts due to their lightweight nature and enhanced stiffness.
- Advantages:
- Lighter than steel wheels
- Improved heat dissipation
- Better aesthetic options
- Disadvantages:
- More expensive than steel
- Can be less durable in extreme conditions
3. Magnesium Wheels
Known for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, magnesium wheels are a premium option, often found on high-performance vehicles.
- Advantages:
- Extremely lightweight
- Enhanced performance characteristics
- Aesthetic appeal with unique finishes
- Disadvantages:
- Very high cost
- Prone to corrosion without proper treatment
- Not suitable for daily driving in harsher climates
4. Carbon Fiber Wheels
Carbon fiber wheels are at the forefront of wheel technology, bringing cutting-edge materials into the automotive realm. They are extremely lightweight but come at a significant price.
- Advantages:
- Unmatched strength and lightweight characteristics
- Excellent vibration dampening
- Highly resistant to corrosion
- Disadvantages:
- Very expensive
- Less availability in standard sizes
- Potential brittleness if not manufactured correctly
Key Terminology in Wheel Construction
Understanding the terminology associated with wheel materials is essential for making informed decisions. Here are key terms to know:
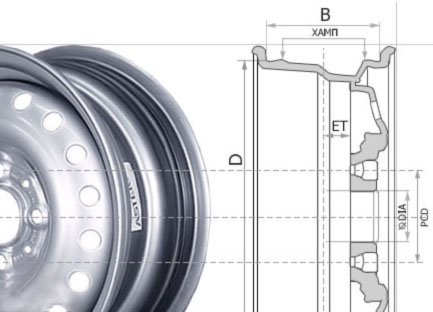
1. Offset
Offset refers to the distance between the wheel’s centerline and the mounting surface of the hub. Proper offset is crucial for proper fitment and handling.
2. Backspacing
Backspacing is the distance measured from the mounting surface to the back edge of the wheel. It influences how the wheel aligns with suspension components.
3. Load Rating
Load rating indicates the maximum weight a wheel can safely carry. This is vital for performance cars that endure additional stress during operation.
4. Bolt Pattern
The bolt pattern specifies the diameter and arrangement of bolt holes on the wheel. Ensuring the correct bolt pattern is essential for compatibility with vehicle hubs.
Choosing the Right Wheel Material
The decision on which material to choose for wheels ultimately depends on various factors such as driving style, budget, and vehicle type. Below is a guide to help in the decision-making process:
1. Driving Conditions
Consider where and how the vehicle will be primarily used:
- Daily Commuting: Steel or aluminum alloy wheels may be more appropriate due to their durability and cost-effectiveness.
- Performance Driving: Aluminum alloy, magnesium, or carbon fiber wheels offer significant advantages for performance-oriented vehicles.
2. Aesthetic Preferences
The visual appeal of wheels can greatly affect the overall look of a vehicle. While steel wheels tend to be more utilitarian, aluminum alloys and carbon fiber can offer a sleek and modern aesthetic.
3. Budget Constraints
Budget is often a pivotal factor when choosing wheels:
- Steel wheels are typically the most affordable option.
- Aluminum alloy wheels provide a balance of performance and affordability.
- Magnesium and carbon fiber wheels come with a premium price tag but offer superior performance benefits for serious enthusiasts.
Conclusion
Understanding the terminology and the characteristics of different wheel construction materials is essential for anyone involved in the automotive world. While the materials used can seem complex, simplifying this knowledge can assist in making informed choices regarding vehicle maintenance, modifications, and performance enhancements. Whether choosing steel for durability, aluminum for performance, or the latest carbon fiber innovations, the right wheels can significantly impact a vehicle’s overall performance and aesthetic appeal.
FAQs
- What is the most common wheel material? Steel wheels are the most common due to their cost-effectiveness and durability.
- Are aluminum alloy wheels better than steel? Aluminum alloy wheels are lighter and often more aesthetically pleasing, but steel wheels may be more durable under harsh conditions.
- What are the benefits of magnesium wheels? Magnesium wheels are extremely lightweight and provide superior performance but come at a higher price point.
- How can wheel weight affect performance? Lighter wheels can improve acceleration and handling, making them preferable for sports and performance vehicles.